Cathode Ray Oscilloscope ( C. R. O. ) | Working and Application of C. R. O
Definition and Basic Details of C. R. O.
A cathode-ray oscilloscope is an instrument which presents signal wave-forms visually.
It is also useful for comparing two signals in phase,frequency or amplitude.
A C.R.O.can operate upto 50 MHz, can allow viewing of signals within a time span of a few
nanoseconds and can provide a number of waveform displays simultaneously on the screen.
It also has the ability to hold the displays for a short or long time (of many hours)so that original signal may be compared with one coming on later.
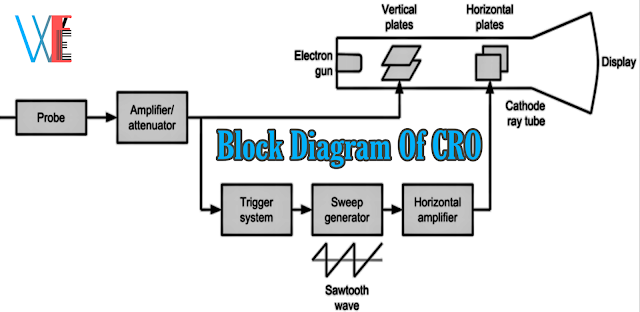
A block diagram of cathode-ray oscilloscope is shown in below figure
Cathode Ray Tube(C.R.T.)
A cathode ray tube is the 'heart of an oscilloscope and is very similar to the picture tube in a television set.
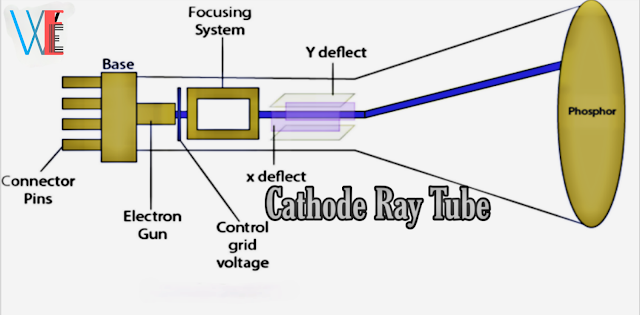
Figure shows the cross-sectional view of
a general-purpose electrostatic C.R.T.
It has the following four major components:
1.An eloctron gun
Electron gun produces a stream of electrons.
2.Focusing and accelerating anodes
They produce a narrow and sharply-focused
beam of electrons.
3.Horizontal and vertical deflecting plates
Horizontal and vertical deflecting plates are use for the path of beam.
4.An evacuated glass envelope with a
phoephorescent screen
It will be produces a bright spot when struck by a high velocity electron beam.
Working of a C.R.O.
When a signal is to be displayed or viewed on the screen it is applied across the Y-plates of a
cathode ray tube.
But to see its waveform or pattern, it is essential to spread it out horizontally from
left to right.
This is achieved by, applying a sawtooth voltage wave to X-plates.
Under these conditions, the electron beam would move uniformly from left to right thereby graphing vertical variations of the input signal versus time.Due to repetitive tracing of the viewed waveform, we get a continuous display because of persistence of vision.
However, to get a stable stationary display on
vertical the screen, it is essential to synchronize the horizontal sweeping of the beam with the input signal across Y-plates.
The signal will be properly synced
only when its frequency equals the sweep-generator frequency.
The usual method of synchronizing the
input signal is to use a portion of the input signal to trigger the sweep generator so that the frequency of the sweep signal is locked or synchronised to the input signal.
It is called internal aync because the synchronization is obtained by internal wiring connections.
Applications of C.R.O.
✓Tracing of an actual waveform of current or voltage.
✓Determination of amplitude of a variable quantity.
✓Comparison of phase and frequeney.
✓In televisions.
✓In radar.
✓For finding B.H.curves for hysteresis loop.
✓For engine pressure analysis.
✓For studying the heart beata, nervous reactions etc.
✓For tracing transistor curves.

Nice
ReplyDelete