What is Instrumentation? And Modes of Measurement
Definition of Instrumentation
The technology of using instruments to measure and control the physical and chemical
properties of materials is called “instrumentation".
When the instruments are used for the measurement and control of industrial manufacturing, conversion or treatment processes, the term process instrumentation is
applied.
When the measuring and controlling instruments are combined so that measurements provide impulses for remote automatic action, the result is called a control system.
Modes of Measurement
There are the three modes of measurement:
1. Primary Measurement
2. Secondary Measurement
3. Tertiary Measurement
All the three modes are described below:
(1) Primary Measurements
In the primary measurement sought value of a parameter is determined by comparing it directly with reference standards.
There is no conversion of measurand in terms of length.
Examples of primary measurement
✓Measurement of time by counting the number of strokes of a clock.
✓Matching of two lengths when determining the length of an object with a ruler.
✓Matching of two colours when judging the temperature of a red hot steel.
(2) Secondary Measurements
In Secondary measurments the indirect measurements involing one translation are
called secondary measurements.
Examples of Secondary Measurments
✓ The pressure measurement by manometers.
✓ The temperature measurement by mercury in glass thermometers.
(3) Tertiary measurements
In Tertiary measurments the indirect measurements involving two conversions are
called tertiary measurements.
Example of Tertiary Measurments:
✓ The measurement of the speed of a rotating shaft by means of an electric tachometer.
Measurements can also be classified as follow:
1. Contact type
In the contact type measurment the sensor of the measuring device contacts the controlled
medium.
2.Non-contact type
In the non contact type measurment the sensor does not contact the controlled medium.
Non-contact measurements include optical, radioactive and others.
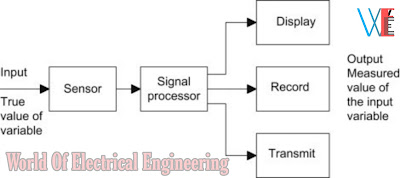
Measurement System and its Elements
Figure 1 shows a measurement generalized system with different components called
elements.
The various elements are mentioned:
1) Primary sensing element
It is an element that is sensitive to the measured variable.
The sensing elements sense the condition, state or value of the process variable by
extracting a small part of energy from the
measurand, and then produce an output which
reflects this condition, state or value of the
measurand.
2) Variable conversion or transducer element
Transducer element converts the signal from one physical form into another without changing the information content of the signal.


Comments
Post a Comment