Percentage Differential Relay and Protection for Power Transformer
The differential protection scheme is used for the protection of transformers having rating 5 MVA and above against internal phase to phase and phase to earth faults.
The basic principle of operation of differential relay is that the vector difference of two or more similar electrical quantities current or voltage goes beyond the specified or the set
value then the relay will operate otherwise the relay will not operate.
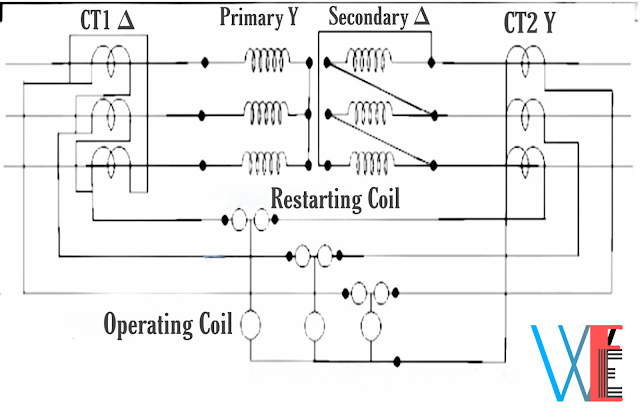
The connection diagram of this type of protection is shown in below figure:
The primary winding of transformer is connected in star and the CTs on that side are connected in delta.
The secondary winding of transformer is connected in delta and the CTs on that side are connected in star.
This prevents the out of balance current flowing through the relay coil due to the phase displacement between the primary and secondary in the healthy condition.
The restraining coil is connected in the pilot wires.
The operating coils are connected between the mid points of the restraining coil and the neutral pilot wire.
Current increases to high value when the transformer feeds the fault outside its
protection zone.
The differential current flows if the characteristics of the CTs are not identical.
But in this case the restraining current also increases so the relay cannot operate.
But when there is internal fault in transformer, the differential current increases and the relay operates.
The differential protection of transformer is also known as Merz-Price protection for the transformer.


Comments
Post a Comment