What is the Wattmeter ? | Types of Wattmeter | Electrical Measurement Theory
Definition
A wattmeter is a combination of an ammeter and a voltmeter and, therefore consists of two
coils known as current coil and pressure coil.
 |
| What is the Wattmeter ? | Types of Wattmeter | Electrical Measurement Theory |
The operating torque is produced due to interaction of fluxes on account of currents in current and pressure coils.
There are following three types of wattmeters:
1.Dynamometer type wattmeter
2.Induction wattmeter
3.Electrostatic wattmeter.
Dynamometer type Wattmeter
Let consider
V= supply voltage
I = load current
R = Resistance of the moving coil circuit.
Current through fixed coils, If = I
Current through the moving coil,
Im = V / R
Deflecting torque,
Td ∝ If × Im = IV / R
For a D.C.circuit the deflecting torque is thus proportional to the power.
The figure of dynamometer type wattmeter is shown in below image 👇 👇
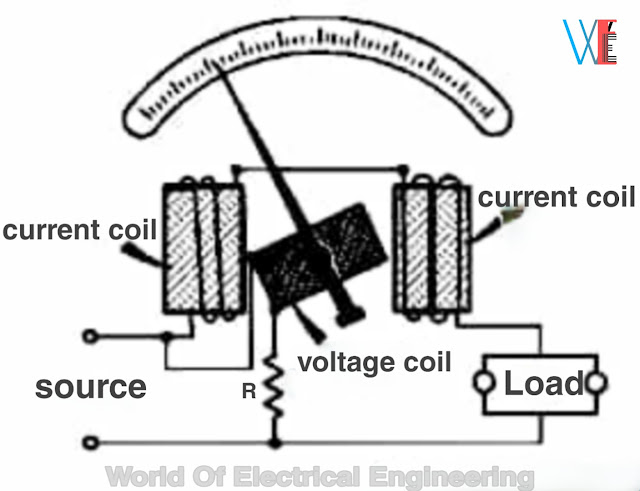 |
| Dynamometer type Wattmeter| types of Wattmeter |
For any circuit with fluctuating torque, the instantaneous torque is proportional instantaneous power.
In this case due to inertia of moving parts the deflection will be proportional to the average
torque, such that the deflection will be proportional to the average power.
For sinusoidally alternating quantities the average power is VI COSØ,
where V= r.m.s.value of voltage
I= r.m.s.value of current
Ø=phase angle between V and I.
Hence an electrodynamic instrument,when connected as shown in figure, indicates the
power, irrespective of the fact it is connected in an A.C.or D.C.circuit.
Scales of such wattmeters are more or less uniform because the deflection is proportional
to the average power and for spring control, controlling torque is proportional to the deflection,
hence, θ ∝ power
Damping is pneumatic.
Induction Type Wattmeters
Induction wattmeters can be used on A.C. circuit only but in contrast with dynamometer wattmeters which can be used both on D.C.and A.C.circuits and are useful only when the frequency and supply voltage are constant.
The figure of induction type wattmeter is shown in below image 👇👇
 |
| Induction type Wattmeter| types of Wattmeter |
The operation of all induction instruments depends on the production of torque due to reaction between a flux Ø1 and eddy
currents induced in a metal disc or drum by another flux Ø2.
Since the magnitude of eddy currents also depends on the flux producing them, the instantaneous value of the deflecting torque is proportional to the square of the current or voltage under measurement and the value of mean deflecting torque is proportional to the mean square of the current or voltage.

Comments
Post a Comment