Measurement of Resistance | Different Methods to Measure Resistance | Measurement of Resistance by MEGGAR
Measurement of Resistance | Different Methods to Measure Resistance | Measurement of Resistance by MEGGAR
Measurement of resistance by Different ways which all the methods are described in this article.
The resistance may be measured by the following methods which all the methods are mentioned below:
(1) Ammeter voltmeter method
This method is mainly applicable to medium resistances and the accuracy is moderate or around 1%.
(2) Ohmmeter
This is an instrument used for directly indicating the value of the unknown
resistance connected across its terminals.
resistance connected across its terminals.
It provides a very quick but moderately accurate means of resistance measurement.
(3) Meggar
This is an instrument for measuring very high resistances such as insulation resistance of the cable.
(4) Wheatstone Bridge
This is the best and the commonest method of measuring medium resistances and measures resistance with a good degree of accuracy.
(5) Kelvin's Double Bridge
This is one of the best method for measurement of low resistances.
(6) Loss of charge method.
This method is particularly suitable for measuring the insulation resistance of a cable because the cable itself may be used as a capacitor provide its capacitance is known.
(7) Murray loop test
This is one of the methods available for location of a ground or a short circuit fault on a cable.
(8) Varley loop test
This is another method for location of faults on cable and is a modification of the Murray loop test.
MEGGAR
Resistance Measurement using MEGGAR
Meggars or megohmmeters are instruments which measure the insulation resistance of
electric circuits relative to earth and one another.
electric circuits relative to earth and one another.
A meggar consists of an e.m.f.source and a voltmeter.
The scale of the voltmeter is calibrated
in ohm such that kilo ohms or megohms, as the case may be.
in ohm such that kilo ohms or megohms, as the case may be.
In measurements the e.m.f.of the selfcontained source must be equal to that of the source
used in calibration.
used in calibration.
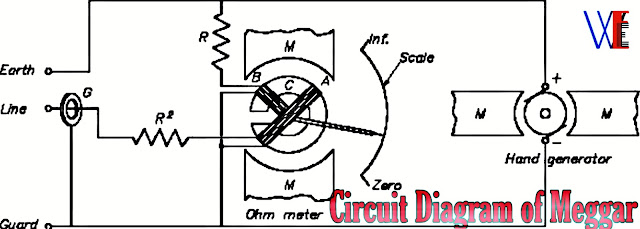
Below Figure shows diagram of a meggar whose readings are independent of the speed of the self-contained generator.
The moving system in-corporates two coils
1.current coil and
2.pressure coil
Which is mounted on the same shaft and placed in the field of a permanent magnet 90° apart.
The generator energises the two coils over
separate wires.
separate wires.
Connected in series with one coil is a fixed resistance R1or several different resistances in order to extend the range of the instrument.
The unknown resistance R is connected in
series with the other coil.
series with the other coil.
The currents in the coils interact with the magnetic field and produce opposing torques.
The deflection of the moving system depends on the ratio of the currents in the coils and is
independent of the applied voltage.
independent of the applied voltage.
The unknown resistance is read directly from the scale of the instrument.
The accuracy of measurement is unaffected by variations in the speed of the generator
between 60 and 180 r.p.m.
between 60 and 180 r.p.m.



WhatsApp trick to hide conversation without deleting and Talibilm provide all news related to study and you can also get info about latest results.
ReplyDelete