Characteristics Of DC Shunt Motor
 |
| Characteristics Of DC Shunt Motor |
- We know that torque is directly proportional to the flux per pole and armature current.
- So, Ta proportional to Φ and Ish
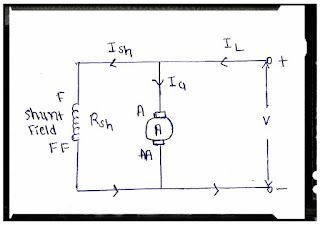
- According to circuit diagram
- Ia = IL - Ish
- Ish = V / Rsh
- V = Eb + Ia Ra
There are three characteristic s of DC Shunt Motor, which is mentioned below.
- Torque - Armature current ( T / Ia ) characteristics
- Speed - Armature current ( N / Ia ) characteristics
- Speed - Torque ( N / T ) characteristics
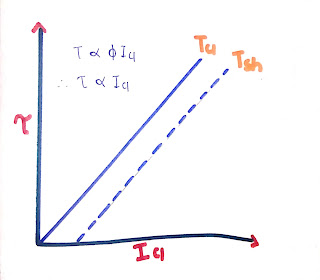
1. Torque - Armature current characteristics
- We know that field current is remains constant because of supply voltage is constant in dc shunt motor.
- Here , for dc shunt motor flux is also constant because supply voltage is kept constant
- So, Ta α Ia
- So torque is directly proportional to the armature current and it's graph is shown in below graph.
 |
| Characteristics Of DC Shunt Motor |
2. Speed - Armature current characteristics
- The formula of back emf for dc motor is given by
Eb = (Φ Z N P)/ ( 60 A)
And Eb = V - Ia Ra
We know that, N α Eb / Φ
So, N α ( V - Ia Ra ) / Φ
- But, we know that flux Φ is constant in DC Shunt Motor.
- So,. N α V - Ia Ra
- By this equation we tell that, if we increases the armature current Ia, so back emf will be decreases and so speed N is decreases slightly, which is shown in below graph.
 |
| Characteristics Of DC Shunt Motor |
3. Speed - Torque characteristics
- We know that the speed of dc motor is given by. N α Eb / Φ
- For dc motor flux Φ is constant
- So, N α Eb α V - Ia Ra and also T α Ia
- So here if armature current Ia increases, then the torque will be increases and Eb decreases so speed will be decreases. Which is shown in below graph.
 |
| Characteristics Of DC Shunt Motor |

Thanks for the equations of a motor!
ReplyDelete