General Layout of Steam Power Plant | Electrical Power Generation
 |
| General Layout of Steam Power Plant | Electrical Power Generation |
Layout of Steam Power Plant
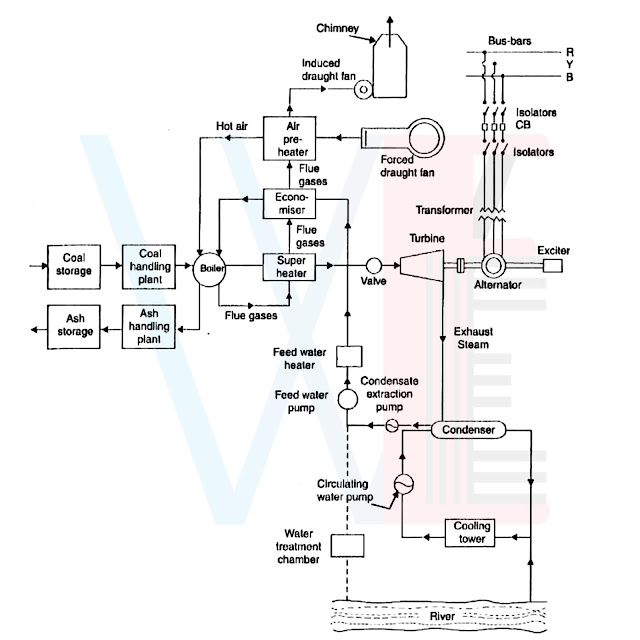
Refer below figure The layout of a modern steam power plant comprises of the following four circuits:
(1) Coal and ash circuit
(2) Ash and gas circuit
(3) Feed water and steam flow circuit
(4) Cooling water circuit.
 |
| General Layout of Steam Power Plant |
(1) Coal and Ash Circuit
Coal arrives at the storage yard and after necessary landing, passes on to the furnaces through the fuel feeding device.
Ash resulting from combustion of coal collects at the back of the boiler and is removed to the ash storage yard through ash handling equipment.
(2) Ash and Gas Cirouit
Ash is taken in from atmosphere through the action of a forced or induced draught fan and passes on to the furnace through the air preheater, where it has been heated by the heat of flue gases which pass to the chimney via the preheater.
The flue gases after passing around boiler tubes and superheater tubes in the furnace pass, through a dust catching device or
precipitator, then through the economiser, and finally through the air preheater before being
exhausted to the atmosphere.
(3) Feed Water and Steam Flow Circuit
In the water and steam circuit condensate leaving the condenser is first heated in a closed feed water heater through extracted steam from the lowest pressure extraction point of the turbine.
It then passes through the deaerator and a few more water heaters before going into the boiler through economiser.
In the boiler drum and tubes, water circulates due to the difference between the density of
water in the lower temperature and the higher temperature sections of the boiler.
Wet steam from the drum is further heated up in the superheater for being supplied to the prime mover.
After expanding in high pressure turbine steam in taken to the reheat boiler and brought to its original dryness or superheated before being passed on to the low pressure turbine.
From there it is exhausted through the condenser into the hot well.
The condensate is heated in the feed heaters
using the steam trapped(bled-steam)from different points of turbine.
A part of steam and water is lost while passing through different components and this is
compensated by supplying additional feed water.
This feed water should be purified before hand, to avoid the scaling of the tubes of the boiler.
(4) Cooling Water Circuit
The cooling water supply to the condenser helps in maintaininga low pressure in it.
The water may be taken from a natural source such as river, lake or sea or the same water may be cooled and circulated once again.
In the latter case the cooling arrangement is
made through spray pond or cooling tower.
Components used in Modern Steam Power Plant
A modern steam power plant comprises of the following components which is mentioned below:
✓ Boiler
> Superheater
> Reheater
> Economiser
> Air-heater
✓ Steam turbine
✓ Generator
✓ Condenser
✓ Cooling towers
✓ Circulating water pump
✓ Boiler feed pump
✓ Wagon tippler
✓ Crusher house
✓ Coal mill
✓ Induced draught fans
✓ Ash precipitators
✓ Boiler chimney
✓ Forced draught fans
✓ Water treatment plant
✓ Control room
✓ Switch yard
Functions of main parts of a steam power plant:
Boiler
Water is converted into wet steam.
Superheater
It converts wet steam into superheated steam.
Turbine
Steam at high pressure expands in the turbine and drives the generator
Condenser
It condenses steam used by the steam turbine.
The condensed steam known as condensate is used as a feed water.
Cooling tower
It cools the condenser circulating water. Condenser cooling water absorbs heat from steam.
This heat is discharged to atmosphere in cooling water.
Condenser circulating water pump
It circulates water through the condenser and the cooling tower.
Feed water pump
It pumps water in the water tubes of boiler against boiler steam pressure.
Economiser
In economiser heat in flue gases is partially used to heat incoming feed water.
Air preheater
In air preheater heat in flue gases which is the products of combustion is partially
used to heat incoming air.

Comments
Post a Comment