Switching Voltage Regulators | Classification of SMPS
The dc output of the rectifier or battery is not regulated. It varies according to the load variations.
 |
| Switching Voltage Regulators | Classification of SMPS |
Switching mode regulators are used to convert unregulated dc to regulated DC output.
The switching mode regulators use dc choppers.
Below figure shows the block diagram of switching mode regulator. The dc chopper takes the input Vs from some unregulated supply.
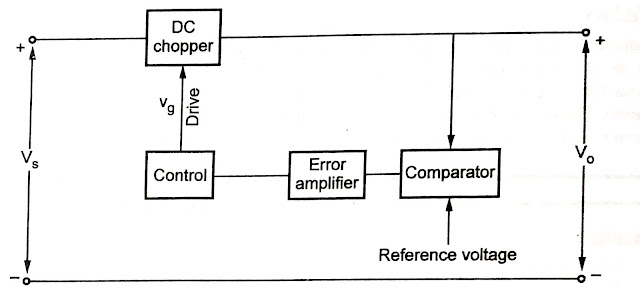 |
| Block Diagram of Switching Mode Regulator |
The chopper may use Transistor, MOSFET, IGBT, SCR or GTO for switching.
The comparator compares the reference voltage with output voltage. The reference voltage is set for the particular output voltage.
The comparator generates the error signal. This error signal acts as the control voltage.
The control block uses the control voltage Vc, to generate the drives of the chopper.
Below figure shows the control waveforms. The control voltage Vc is compared with the sawtooth waveform.
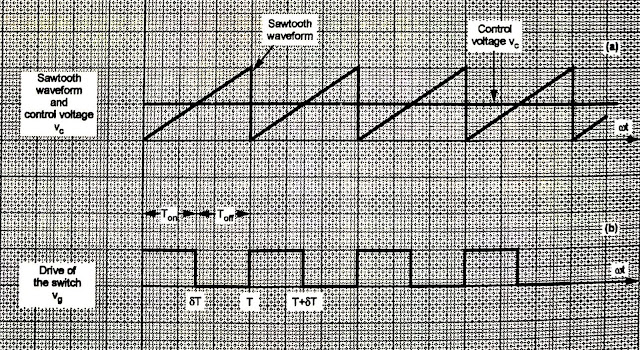 |
| Waveforms of Switching voltage Regulators |
The result of comparison is the drive of the chopper as shown in second waveform. This drive is given to the switch in the chopper.
The sawtooth waveform is generated by an oscillator in the control circuit.
The frequency of the sawtooth waveform decides the switching frequency of the chopper.
Normally the switching period is 100 times longer than the switching time of the switch.
Excessive switching frequencies may increase losses in the chopper.
The filters are normally used in the output to make the output voltage ripple free and smooth.
The regulation is also improved.The width of the drive is continuously adjusted to regulate output voltage.
Hence it is also called as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)control.
Classification of SMPS
Classification of SMPS is mentioned below:
1. SMPS
(A) Isolated Converters
(B) Non isolated Converters
(A) Isolated Converters
✓ Unidirectional Core Excitation
1. Flyback Converter
2. Forward Converter
✓ Bidirectional Core Excitation
1. Push-Pull Converter
2. Half Bridge Converter
3. Full Bridge Converter
(B) Non isolated Converter
1. Buck Regulator
2. Boost Regulator
3. Buck Boost Regulator
3. Cuk Regulator

Comments
Post a Comment