Surge Impedance Loading or SIL - Definition, Formula
 |
| Surge Impedance Loading or SIL - Definition, Formula |
What is Surge Impedance Loading?
Surge Impedance Loading or SIL is the power demand or load supplied by the transmission line having no resistance by considering unity load power factor.
Explanation of Surge Impedance Loading or SIL
In case of transmission line surge Impedance Loading is depends on inductance and capacitance of the transmission line.
Formula of Surge Impedance Loading or SIL
Where, L - Inductance of transmission Line
C - Capacitance of transmission Line
Surge Impedance Loading is independent of the transmission line length.
In this case I^2 X of the transmission line provides charging kVA of the transmission line.
SIL or Surge Impedance Loading can also be given as below formula:
Formula of Surge Impedance Loading or SIL
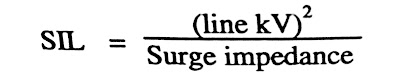 |
| Formula of Surge Impedance Loading or SIL |
From SIL or Surge Impedance Loading, one can calculate power demand or load supplied by transmission line at various voltage levels.
Useful Electrical Engineering Articles:
Useful Electrical Engineering Articles:
- How Potentiometer Works ? | Various Types of Potentiometer
- Do you know what is ELCB and how it works?!!!
- Comparison Between Fuse and MCB !!!
- How M.C.B. works???!!!
- Various Types of Fuse!!!
- How Fuse is work??!!
- Construction of Cable and It's Classification
- Characteristics Of DC Shunt Motor
- What is Electric Drives And Block Diagram of It
- Coulomb's Law
- Kirchoff's Law
- How Galvanometer Works?
- Types of DC Motor
- How DC Motor Works?
- Types Of DC Generator
- High Temperature Alarm Device
- Magnetic Power Generation
- How Voltmeter works?
- What is Diode ? And How it works?
- MarX Generator>> High Voltage Pulse Generator
- What is capacitor? And How it works?
- How Inductor Works?

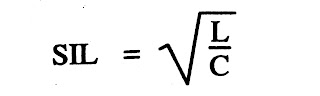
Comments
Post a Comment