Steam Power Plant
Generally, thermal power plant is one which is used to produce electrical power on a large scale.
A steam power plants are used in which the chemical energy of a fuel is utilized to generate high pressure, high temperature steam in a boiler.
Which steam is used in a turbine to produce mechanical power which is finally converted into electrical energy by an alternator.
This is represented by a simplified block diagram, which is shown in below figure. Fuel used may be coal,oil or natural gas.
In a steam power plant, various heat recovery systems like air pre-heater, Economiser are used to improve the thermal efficiency in the steam power plant.
Various components of a steam
power plant with their function are explained below:
 |
| Steam Power Plant |
Which steam is used in a turbine to produce mechanical power which is finally converted into electrical energy by an alternator.
This is represented by a simplified block diagram, which is shown in below figure. Fuel used may be coal,oil or natural gas.
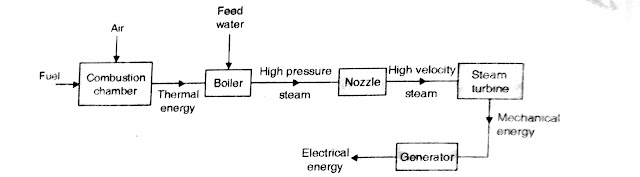 |
| Block Diagram for energy conservation in steam power plant |
Various components of a steam
power plant with their function are explained below:
(1) Blower:
Function of the blower is to draw the surrounding air needed for combustion of fuel in the steam power plant. The air drawn by blower is supplied to air pre-heater.
(2) Air pre-heater:
Air pre-heater is a heat transfer device in which the air drawn from surroundings is heated with the
help of hot flue gases before discharged to atmosphere through the chimney.
The heated air is supplied to the furnace.It improves the combustion efficiency of the fuel.
(3) Furnace:
Heated air from air pre-heater is supplied to the furnace where fuel is burnt, The products of combustion of fuel and air are called flue gases.
(4) Economiser:
The feed water before supplied to the boiler tubes is heated with the help of flue gases. lt reduces the energy needed for formation of steam.
(5) Boiler:
lt consists of boiler shell, water, tubes and superheater.
The Feed water supplied from the economiser is first converted into wet steam in water tubes and then into superheated steam in the superheater due to the heat supplied by the hot flue gases.
Steam is generated at high pressures in the boiler.
 |
| Steam Power Plant |
(6) Steam Turbine and Generator:
High pressure, superheated steam of the boiler expands in the turbine and produces the mechanical work.
This work is utilised to drive a generator which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(7) Condenser and condensate extraction pump:
Steam from steam turbine is exhausted to the condenser where the steam is condensed by rejecting heat to cooling water.
condensed steam is called the condensate which is drawn with the help of condensate extraction pump and which is supplied to hot-well.
(8) Feed pump:
The condensate collected in the hot well with make up water is fed back with the help of feed pump at boiler pressure to the economiser.
(9) Cooling tower:
The Cooling water from cooling tower is circulated into the condenser and absorbs heat from the exhaust steam of the steam turbine.
Resultant heated water which comes from condenser is supplied at the top of cooling tower.
This heated water falls through the nozzles.It gets cooled by the cool air passed from the bottom of cooling tower.The heated air is discharged to the surroundings from the top of cooling tower.
(10) Condenser water circulating pump:
This pump circulates the cooling water from to the cooling tower to the condenser and the heated water from the condenser back to the cooling tower.

Comments
Post a Comment