Design of Submersible Motor
Submersible motor is used to drive the submersible pump. Submersible motor is also a squirrel cage type induction motor.
Its principle and the general construction is similar to the squirrel cage type induction motor.
It means there is laminated stator core and three phase winding in it and there is squirrel
cage rotor.
cage rotor.
But as the whole motor is under water, special type of construction has to be employed.
Mainly all the parts are made of the corrosion resistance type materials. Its diameter is
less and the axial length is more.
less and the axial length is more.
Instead of using the ordinary bearings the thrust bearings are used.
There are two types of construction
of the submersible motor.
(1) Wet type submersible motor:
This type of motor is completely filled with clean water or oil or emulsion of water and oil.
(2) Dry type submersible motor:
In this type of motor the stator winding is dry and other parts are filled with clean water or oil or emulsion of water and oil.
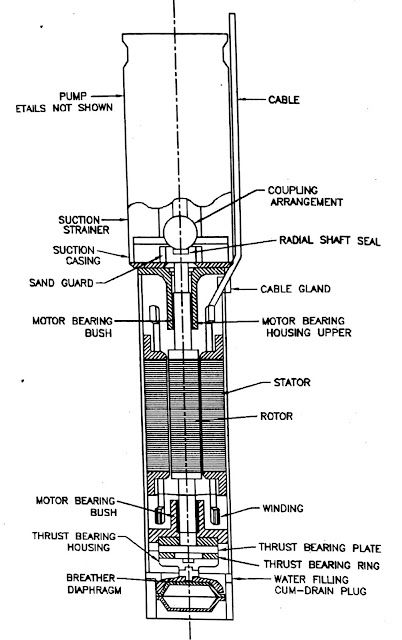
Construction:
All the parts of the motor should be of corrosion resistance type and should posses the mechanical performance so that these are able to work continuously under water.
Different parts and their materials
are given in below Table:
are given in below Table:
(a) Frame of motor:
Frame of the motor is made of cast iron. Casting should be strong and without crack. If necessary the pressure testing of the casting
should be done for crack detection.
should be done for crack detection.
Stator: Stator is made of electric sheet steel.
(b) Stator winding:
Stator winding is made of high conductivity annealed copper conductors insulated with PVC.
It should confirm to IS: 8783-1978 and should be appropriate for wet type motor working
under water.
under water.
For other type of submersible motor, the stator winding should be made of high conductivity
annealed copper conductors and insulated with enamel.
annealed copper conductors and insulated with enamel.
It should confirm to IS: 4800(Part- VII)-1970. This standard shows specifications of round winding wires with good dielectric properties used in wet condition.
(c) Shaft and rotor:
Shaft is made of carbon steel. Rotor laminations are fitted on the shaft and copper bars are embedded in the slots.
These rods are short circuited at the two ends by copper short circuiting rings. Dynamic balancing of the rotor is done.
Proper epoxy paint is applied on the rotor so that there is no corrosion of the rotor due to water.
(d) Bearings:
(1)Thrust bearings:
Thrust bearing should be provided in the motor so that it can bear the weight of all the rotating parts and the hydraulic thrusts produced in the operating range.
It should be properly lubricated. Housing of the thrust bearing is made of cast iron and the bearing plate is made of bronze and the bearing ring is made of graphite.
Drain plug is provided in the thrust bearing so that oil or water filled in thrust bearing housing or motor can be drained off.
(2)Radial bearing:
Before installing the pump set, radial bearing of the rotary shaft should be lubricated with the clean water or oil.
Protection against external impurities:
Motor should be protected by using cable gland rubber seal, etc. so that water of the bore well, sand and other impurities are prevented
from entering the motor.
from entering the motor.
Breathing attachment:
Breathing attachment like bellow, diaphragm etc. should be used with motor so that the change in volume produced due to the change in temperature can be compensated.
Earthing:
Earthing of the motor should be done as per IS:3034 - 1966. Earthing of the motor can also be done with the discharge pipe.
Submersible cable:
Cable for submersible motor should be of PVC insulated PVC sheathed type and should confirm to IS: 694 - 1977.
Size of the inner conductor should be sufficient
for the use in air and in water. Consumer should specify the length of the cable required.
for the use in air and in water. Consumer should specify the length of the cable required.
If it is not specified, 3 m length or cable is provided with motor. If the cable joint is required the manufacturer should provide
the method of making water tight joint.
the method of making water tight joint.
Size and the length of the cable should be selected such that voltage drop up to the motor
terminal should not exceed 3 %.
terminal should not exceed 3 %.
Ratings of motor:
Voltage ratings of the submersible motor should confirm to IS:585-1962. Frequency should be equal to the standard frequency such that 50 HZ.
Change in the voltage and frequency for category A motor should be as per IS: 325 -1978 or as per IS: 996 - 1979 and for category B motor should be as per IS: 7538 - 1955.
(1) Preferred output ratings:
Preferred output ratings should be as per IS:325 - 1978 or as per IS: 996 - 1979.
(2) Speed ratings:
Preferred synchronous speed is 1500 rpm or 3000 rpm.
(3) Rating plate:
The following information is given on the name plate of the motor.
✓ Reference of Indian standards(IS:9283-1979)
✓ Induction motor
✓ Name of the manufacturer
✓ Number of manufacturer and frame reference
✓ Type of duty
✓ Frequency in HZ.
✓ No.of phases
✓ Rated output in kW
✓ Rated voltage and winding connection
✓ Approximate current at rated output
✓ Speed in rpm at rated output
✓ Category of voltage and frequency variations.
For convenient identification, number or manufacturer should be punched on the rating plate.



Very informative article
ReplyDeletehello dear, your blog such a nice and very informative. thanks for providing us. Submersible Pumps manufacturers
ReplyDelete