Types Of Electric Drive
 |
| Types of Electric Drive |
Electric drive can be classified into following categories:
(i) Group drive
(ii) Individual drive
(iii) Multi motor drive.
This is also known as line shaft drive. A big size motor(main motor)drives a common
shaft.
To this shaft, numbers of small machines are connected. Thus a common shaft drives the
small machines.The small machines are connected the common shaft by means of multi stepped pulleys as shown in below Figure.
✓ Single motor of big capacity is used so there is considerable saving in cost.
✓ Maintenance is less.
✓ Efficiency and power factor is better if the motor operates near rated capacity.
✓ If machines are overloaded, the group drive is advantageous because the overload occurring for main motor is very less.
✓ Any fault on main motors causes stopping of all small machines connected to the common shaft.
✓ Machine has to be installed at places which is convenient for shafting.
✓ There is no flexibility of layout i.e, shifting of a small machine from one location to other is hardly possible.
✓ If only few numbers of machines are needed to be operated, the main motor operates with a very less capacity hence its efficiency and power factor is poor.
✓ The appearance due to shaft, pulleys etc. are not good.
✓ Speed control of individual small machine is cumbersome.
✓ Considerable amount of power is wasted in power transmission.
✓ Noise level is high.
✓ Future expansion is hardly possible.
Group drive is adopted when existing factories are changed over from engine drive to electric motor drive.
Individual machine is fitted with its own motor such that drilling machine, lathe machine etc.
Each operator has complete control of his machines.
✓ Flexibility in layout.
✓ Each machine operates near to rated capacity so efficiency and power factor is better.
✓ Fault on any one machine does not create problem for other machines.
✓ The appearance of layout is good.
✓ It is economical on long term basis.
✓ Speed control of individual machine is easily possible.
✓ Future expansion is possible.
✓ level is comparatively less.
✓ High initial cost
✓ Power loss in transmission.
In multi motor drive, separate motors are used for operating different parts of same mechanism.
i.g. in case of overload crane, different motor are used for hoisting for up and down motion, long travel motion and cross travel motion.
(i) Group drive
(ii) Individual drive
(iii) Multi motor drive.
- 1. Group Drive:
This is also known as line shaft drive. A big size motor(main motor)drives a common
shaft.
 |
| Diagram of Group Drive |
To this shaft, numbers of small machines are connected. Thus a common shaft drives the
small machines.The small machines are connected the common shaft by means of multi stepped pulleys as shown in below Figure.
- Advantages of group drive
✓ Single motor of big capacity is used so there is considerable saving in cost.
✓ Maintenance is less.
✓ Efficiency and power factor is better if the motor operates near rated capacity.
✓ If machines are overloaded, the group drive is advantageous because the overload occurring for main motor is very less.
- Disadvantages of group drive
✓ Any fault on main motors causes stopping of all small machines connected to the common shaft.
✓ Machine has to be installed at places which is convenient for shafting.
✓ There is no flexibility of layout i.e, shifting of a small machine from one location to other is hardly possible.
✓ If only few numbers of machines are needed to be operated, the main motor operates with a very less capacity hence its efficiency and power factor is poor.
✓ The appearance due to shaft, pulleys etc. are not good.
✓ Speed control of individual small machine is cumbersome.
✓ Considerable amount of power is wasted in power transmission.
✓ Noise level is high.
✓ Future expansion is hardly possible.
Group drive is adopted when existing factories are changed over from engine drive to electric motor drive.
- 2. Individual Drive:
Individual machine is fitted with its own motor such that drilling machine, lathe machine etc.
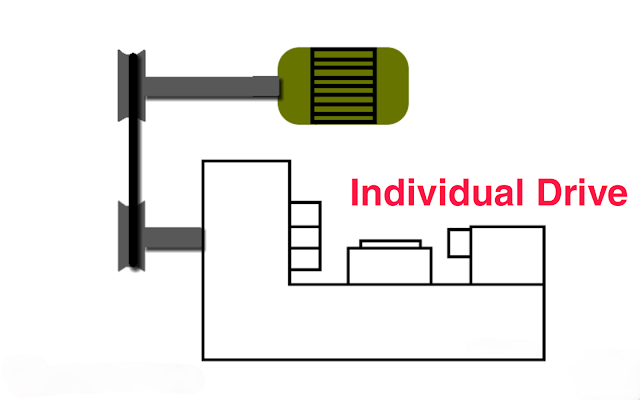 |
| Diagram of individual Drive |
Each operator has complete control of his machines.
- Advantages of Individual Drive:
✓ Flexibility in layout.
✓ Each machine operates near to rated capacity so efficiency and power factor is better.
✓ Fault on any one machine does not create problem for other machines.
✓ The appearance of layout is good.
✓ It is economical on long term basis.
✓ Speed control of individual machine is easily possible.
✓ Future expansion is possible.
✓ level is comparatively less.
- Disadvantages of Individual Drive
✓ High initial cost
✓ Power loss in transmission.
- 3. Multimotor Drive:
In multi motor drive, separate motors are used for operating different parts of same mechanism.
 |
| Diagram of multimotor Drive |
i.g. in case of overload crane, different motor are used for hoisting for up and down motion, long travel motion and cross travel motion.

I'm blown away by the little print you've provided regarding signs. It is an enlightening article for both myself and others. Thank you for bringing such interesting topics to our attention. pipeline industries
ReplyDelete